Learn how to effectively manage and treat osteomyelitis with this comprehensive guide. Understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Introduction
Osteomyelitis is a serious infection of the bone that can cause significant pain, disability, and complications if not properly managed. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of osteomyelitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and effective management strategies. By gaining a deeper understanding of this condition, individuals and healthcare professionals alike can work together to optimize patient outcomes and improve quality of life.
What is Osteomyelitis?
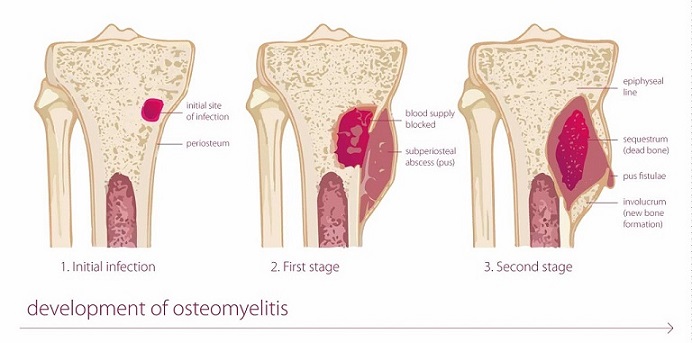
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection that occurs when bacteria or fungi invade the bone tissue. It can affect any bone in the body, but most commonly occurs in the long bones of the arms and legs, the spine, or the pelvis. This infection can be acute or chronic, with chronic cases often being more challenging to treat.
Causes of Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis can arise from various causes, including:
- Bacterial Infection: The majority of osteomyelitis cases are caused by bacteria, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common culprit. Other bacteria, such as Streptococcus and Escherichia coli, can also contribute to the infection.
- Direct Bone Contamination: Open fractures, surgical procedures, and traumatic injuries that expose the bone to bacteria can lead to osteomyelitis.
- Bloodstream Infection: Bacteria can travel through the bloodstream from another infection site, such as a urinary tract infection or pneumonia, and reach the bone, causing osteomyelitis.
Symptoms of Osteomyelitis
Recognizing the symptoms of osteomyelitis is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Persistent bone pain
- Swelling and redness around the affected area
- Limited range of motion
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue and malaise
- Open sores or draining pus in severe cases
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to prevent further complications.
Diagnosing Osteomyelitis
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management of osteomyelitis. Healthcare professionals employ several diagnostic methods to confirm the presence of the infection and determine its severity. These include:
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing osteomyelitis involves a thorough medical history review and physical examination. The healthcare provider will inquire about symptoms, past medical conditions, recent infections, and any previous bone injuries or surgeries. During the physical examination, they will assess the affected area for tenderness, swelling, and signs of infection.
Laboratory Tests
Various laboratory tests can aid in diagnosing osteomyelitis. These include:
- Blood Tests: Complete blood count (CBC) may reveal an elevated white blood cell count, indicating an active infection. Blood cultures can help identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
- Bone Cultures: A bone biopsy or aspirate may be performed to obtain a sample of bone tissue or pus for culture. This helps identify the causative organism and determine appropriate antibiotic treatment.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans can provide detailed images of the affected bone, revealing any signs of infection, bone damage, or abscess formation.
FAQs about Osteomyelitis
1. What are the risk factors for developing osteomyelitis?
Several factors increase the risk of developing osteomyelitis, including:
- Diabetes
- Peripheral artery disease
- Recent trauma or surgery involving the bone
- Intravenous drug use
- Compromised immune system
2. Can osteomyelitis be prevented?
While it may not always be preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing osteomyelitis. These include practicing good hygiene, promptly treating any wounds or infections, managing chronic conditions effectively, and adhering to proper surgical techniques.
3. How is osteomyelitis treated?
Treatment for osteomyelitis typically involves a combination of antibiotics, surgical intervention (if necessary), and supportive therapies. Antibiotics are administered intravenously to combat the infection, and surgical procedures may involve draining abscesses, removing infected bone, or providing adequate blood supply to the affected area.
4. How long does it take to recover from osteomyelitis?
Recovery from osteomyelitis can vary depending on the severity of the infection and individual factors. Treatment can last from several weeks to several months, and close monitoring is essential to ensure complete resolution of the infection.
5. What are the potential complications of osteomyelitis?
If left untreated or not managed effectively, osteomyelitis can lead to serious complications such as:
- Bone death (osteonecrosis)
- Spread of infection to surrounding tissues
- Formation of chronic draining sinus tracts
- Limb amputation (in severe cases)
6. Can osteomyelitis recur?
Yes, osteomyelitis can recur, especially if the underlying risk factors are not adequately addressed. Close follow-up with healthcare professionals, adherence to treatment plans, and vigilant management of any contributing conditions can minimize the risk of recurrence.
Conclusion
Osteomyelitis is a complex and potentially debilitating bone infection that requires prompt and effective management. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can improve their chances of successful treatment and recovery. Collaboration between patients, healthcare professionals, and researchers remains essential in enhancing our understanding of osteomyelitis and advancing treatment options. Remember, early detection and intervention are key to mitigating the risks and consequences of osteomyelitis.




No Comment! Be the first one.