Discover the causes, symptoms, and treatments for sickle cell ulcers. Learn how to manage this condition effectively for improved healing and pain relief.
Introduction
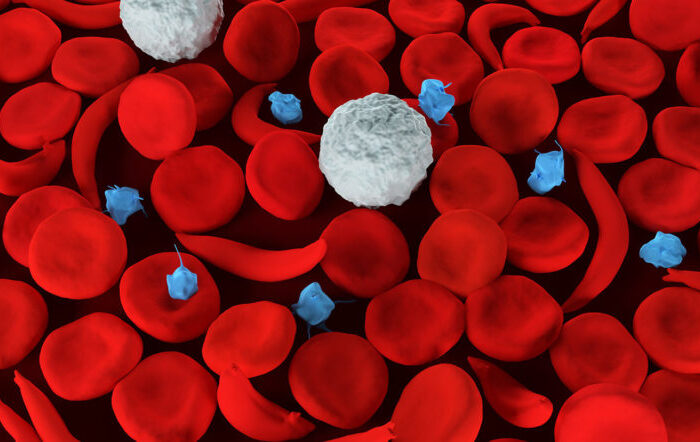
Sickle cell ulcers are a challenging condition that affects individuals with sickle cell disease. These ulcers occur due to the abnormal shape of red blood cells, which can cause blockages in blood vessels, leading to tissue damage and the development of painful ulcers. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available for sickle cell ulcers.
Causes of Sickle Cell Ulcers
Sickle cell ulcers develop as a result of several factors related to sickle cell disease. The underlying cause is the presence of hemoglobin S, an abnormal form of hemoglobin found in red blood cells of individuals with sickle cell disease. Here are the main causes of sickle cell ulcers:
- Abnormal Hemoglobin: Sickle cell ulcers result from the presence of hemoglobin S, which causes red blood cells to become rigid and take on a crescent or “sickle” shape. This abnormal shape hinders blood flow and damages tissues.
- Vascular Occlusion: The sickle-shaped red blood cells can block small blood vessels, leading to reduced blood flow and tissue damage. This lack of proper blood circulation contributes to the development of ulcers.
- Inflammation and Infection: Tissue damage caused by reduced blood flow can create an environment conducive to inflammation and infection, further complicating the healing process of ulcers.
Symptoms of Sickle Cell Ulcers
Identifying the symptoms of sickle cell ulcers is crucial for early intervention and effective management. The following symptoms are commonly associated with this condition:
- Painful Ulcers: Sickle cell ulcers are characterized by painful, open sores or lesions that typically occur on the lower legs and feet. The pain can range from mild to severe, and it may persist for an extended period.
- Slow Healing: Due to the impaired blood circulation in individuals with sickle cell ulcers, the healing process is often slow and may be further hindered by inflammation and infection.
- Skin Changes: The skin around the ulcers may exhibit various changes, such as discoloration, swelling, and a shiny or glossy appearance.
- Fever: In some cases, sickle cell ulcers can lead to an accompanying fever, indicating the presence of an infection.
- Restricted Mobility: Severe pain and discomfort from the ulcers can limit mobility, making it challenging for individuals to walk or engage in regular activities.
- Fatigue: The ongoing pain and physical stress associated with sickle cell ulcers can contribute to fatigue and a general feeling of weakness.
How to Treat Sickle Cell Ulcers
Managing sickle cell ulcers involves a comprehensive approach to relieve symptoms, promote healing, and prevent complications. Here are some effective treatment options:
- Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential for managing sickle cell ulcers. This includes regular cleaning, dressings, and the use of specialized wound care products to maintain a clean and moist environment for optimal healing.
- Pain Management: Controlling pain is a crucial aspect of treating sickle cell ulcers. Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications may be recommended, depending on the severity of the pain.
- Compression Therapy: Compression stockings or bandages can help improve blood circulation and reduce swelling, thereby aiding the healing process.
- Preventing Infection: Since infection can further complicate the healing process of sickle cell ulcers, it is important to take preventive measures. This includes practicing good hygiene, keeping the affected area clean, and promptly treating any signs of infection.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is present or suspected, antibiotics may be prescribed to combat the infection and prevent its spread.
- Topical Medications: Certain topical medications, such as antibiotic ointments or creams, can be applied directly to the ulcers to promote healing and prevent infection.
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases where conservative measures are not effective, surgical interventions may be considered. This can involve procedures such as debridement (removal of dead tissue), skin grafts, or other surgical techniques to promote healing and improve the condition of the ulcers.
- Blood Transfusions: In some instances, blood transfusions may be necessary to increase the number of healthy red blood cells and improve overall blood circulation, which can aid in the healing of ulcers.
- Hydroxyurea: Hydroxyurea is a medication that can help reduce the frequency and severity of painful episodes and ulcers in individuals with sickle cell disease. It works by increasing the production of fetal hemoglobin, which prevents the formation of sickle-shaped red blood cells.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making certain lifestyle modifications can also contribute to managing sickle cell ulcers effectively. This includes staying hydrated, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding triggers that can cause pain crises, and engaging in regular exercise to promote overall health and well-being.
FAQs about Sickle Cell Ulcers
1. Can sickle cell ulcers be prevented? While it may not be possible to completely prevent the development of sickle cell ulcers, certain measures can help reduce the risk. These include proper management of sickle cell disease, regular wound care, and early intervention for any signs of infection or complications.
2. Are sickle cell ulcers contagious? No, sickle cell ulcers are not contagious. They are a complication of sickle cell disease and are not spread through contact with an affected individual.
3. How long does it take for a sickle cell ulcer to heal? The healing time for sickle cell ulcers can vary depending on the individual, the size and severity of the ulcers, and the effectiveness of the treatment. In general, it can take several weeks to months for the ulcers to heal completely.
4. Are there any complications associated with sickle cell ulcers? Yes, if not properly managed, sickle cell ulcers can lead to various complications. These include infection, chronic non-healing ulcers, scarring, and limited mobility.
5. Can sickle cell ulcers recur? Yes, individuals with sickle cell ulcers may experience recurrent episodes, especially if the underlying sickle cell disease is not well-controlled or if there are triggers that can lead to vaso-occlusive crises.
6. Can natural remedies help in the treatment of sickle cell ulcers? While natural remedies may provide some relief from symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate medical treatment. Natural remedies should not be used as a substitute for evidence-based medical care.
Conclusion
Sickle cell ulcers can be a challenging and painful condition for individuals with sickle cell disease. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking timely medical intervention are crucial for effective management. With proper wound care, pain management, and treatment options such as compression therapy, antibiotics, and surgical interventions, individuals with sickle cell ulcers can experience relief, improved healing, and a better quality of life with sickle cell disease. It is important to follow a comprehensive approach that includes maintaining good hygiene, managing pain, preventing infection, and considering surgical interventions when necessary. Additionally, lifestyle modifications and medications like hydroxyurea can help in managing the condition and reducing the frequency and severity of ulcers.




No Comment! Be the first one.